The operation of the SLR camera, the different focusing systems of the physical camera, the different parts of a camera are often not well known by amateur photographers.
Knowing how light exposes on the camera, how a camera lens works help to use indispensable accessories like filters and flashes, for example.
A camera diagram shows you in detail how the camera of a smartphone works like a DSLR, except for some details.
The history of the camera through the pinhole allows to understand the essence of photography.
A camera is a darkroom with a hole to let the light in.a hole that will focus the light rays and a receiver capable of reacting to the light.this darkroom is found in all cameras, compact or reflex, silver or digital!
For the youngest, I remind you that a film camera is a traditional camera using a film to record the image, which must then be developed with chemical products to obtain the photo.
Compact or SLR, same fight!
This is an SLR camera but on a compact camera it’s the same thing… We have this part between the lens… This is the lens… We have this part which corresponds to the darkroom… At the bottom the sensor : it can be a silver film or a digital sensor.

La chambre noire et les éléments communs à tous les appareils photo
A shutter system keeps the film or sensor protected from light when not in use.
This shutter is placed just in front of the sensor and at this moment it is called a focal plane shutter because it is just in front of the plane where the image is formed, on what is called the focal plane.
To understand what happens, you need to know the construction of an image, but this is beyond the scope of this course! Otherwise there are shutters placed in the lens, called a central shutter.
A lens is a set of lenses whose role is to focus the light rays captured by the system, in fact what corresponds to the pinhole.
The diaphragm
The hole of the pinhole corresponds to the diaphragm that regulates the opening and therefore the size of the hole in the lens. When the lens is well made, it is in this place, in the center of the lens, that the light rays will cross and be projected in the darkroom.
This is where the diaphragm is placed and in the case of a central shutter, we will try as far as possible to place it as close as possible to this optical center, the center of the lens. In the case of a reflex camera, the sight is done by a reflection on a mirror.
The viewfinder to see the real image
The advantage of the reflex system is to be able to observe directly the image formed by the lens.
This image formed by the lens is projected and reflected in a prism to end up in the viewfinder and the eye of the photographer.
It is much more complex than this diagram! It would be necessary to make a diagram in three dimensions to follow the path of the image in the camera!
The image is projected onto the mirror…from the mirror it is projected up into the prism…then either onto the right side or the left side of the prismI’m going to assume it is projected onto the right side…once projected onto the right side, the image is sent back to the left side…from the left side of the prism it is sent back to the front side and from the front side to the viewfinder!
The path of light in an SLR camera!
We will see in a next view the operation of the mirror! At the time of the release, the mirror rises, the light no longer reaches the sensor.

As the mirror is raised, the light is no longer sent to the viewfinder. During the shooting the photographer does not see anything in the viewfinder! This view in the viewfinder of the real image was really the prerogative of these reflex cameras.
They were the only cameras at the time of film capable of showing the photographer the image actually recorded by the camera.
Today with digital cameras, whether it is an SLR like this one, a hybrid or a compact, the image is formed in the electronic viewfinder from the image recorded by the digital sensor.
See the real picture
The digital sensor being in direct vision, there is no mirror on a compact or a hybrid and it is indeed the image formed by the lens that we observe on the screen or in the viewfinder.Any digital camera today shows the image formed by the lens.All cameras today are exactly on the same plane we have exactly the same sight by the lens!The interest of the SLR is no longer so obvious and even its system with a noisy mechanical mirror is no longer necessary! The SLR is even becoming anachronistic and it is a system, a type of camera that is bound to disappear, replaced by what is currently called mirrorless cameras (Mirror less) or more commonly the “hybrids”.
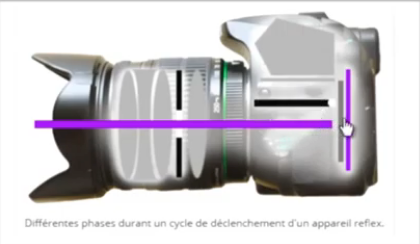
Trigger cycle
Here is a detailed description of how the SLR works at the moment of release:
- 1 – the diaphragm closes at its true working value
- 2 – the mirror rises
- 3 – the light reaches the shutter
- 4 – the shutter opens and the light reaches the sensor
- 5 – the sensor records the image projected by the lens
- 6 – at the end of the exposure the shutter closes
- 7 – the mirror comes down
- 8 – the sight is restored in the viewfinder
- 9 – the diaphragm opens to provide a clear view in the camera’s viewfinder.
As you can see, it is a whole cycle which is done very quickly but which still requires a certain amount of time, hence a certain delay in triggering even on an SLR!
That is to say that when we trigger we must anticipate on the very fast actions to counter this slight defect of the reflex, even if today, the delay in triggering is very low!
This delay is real, not thinking about it, forgetting to take it into account is a source of disappointment in action photography!
In the next video, we will see the different sensors, their advantages and disadvantages!
Don’t forget to subscribe to the channel to be warned of the next videos ! Click on the bell ! If you liked it, please put a nice thumb !
For a perfect mastery of your camera on a daily basis, I propose you a series of simple exercises to practice, to get it, click on this link !
I hope this talk on how the camera works makes you more friendly with your gear! Please consider commenting and sharing with your friends!